Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
入澤 恵理子; 加藤 千明
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 591, p.154914_1 - 154914_10, 2024/04
被引用回数:0核燃料再処理施設における濃縮運転時の溶液組成及び沸騰の変化を考慮して、オーステナイト系ステンレス鋼R-SUS304ULCの腐食量を評価した。オーステナイト系ステンレス鋼R-SUS304ULCは、日本の使用済燃料再処理施設の高放射性廃液濃縮装置の構造材料であり、濃縮運転時に腐食性の高い硝酸溶液を処理する。本研究の結果、カソード反応活性化によるステンレス鋼の腐食速度を加速する要因として、硝酸濃度、酸化性金属イオン濃度、減圧沸騰に着目する必要があることがわかった。
村上 健太*; 鬼沢 邦雄; 山本 章夫*
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 66(4), p.199 - 202, 2024/04
, 66(4), p.199 - 202, 2024/04
日本原子力学会標準委員会は、高経年化対策実施基準の改定を通して長期運転にかかる活動をリードしてきたが、最近の法・規制の変更を踏まえて、引き続き重要な貢献をする必要があると考えている。本稿は、2023年秋の大会で実施された企画セッションにおける議論を再構成し、安全な長期運転に向けた取り組みとその標準化における留意点を解説したものである。重要な点として、(1)時間の経過に伴って見いだされる知識を有効に活用すること、(2)オブソレッセンスを含む安全への影響が大きな新知見を見逃さないこと、(3)安全への影響と発現可能性の大きさを踏まえて対応に重要度をつけること、(4)国際的な知識基盤構築へ貢献することなどが挙げられる。
関 暁之; 吉川 雅紀; 西野宮 良太*; 沖田 将一朗; 高屋 茂; Yan, X.
Nuclear Technology, 12 Pages, 2024/00
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)原子力プラントの安全な運転を支援するため、2種類のディープニューラルネットワーク(DNN)のシステムを構築した。一つは、原子力プラントの各種物理量についてシミュレーションよりも数桁少ない計算時間で推定するサロゲートシステム(SS)である。もう一つは、物理量から異常の原因となる外乱の状態を推定するシステム(ASIS)である。両システムとも、高温工学試験研究炉(HTTR)の挙動を様々なシナリオで再現することができる解析コード(ACCORD)から得られたデータを用いて学習を行った。DNNのモデルは、主要なハイパーパラメータを調整することにより構築された。これらの手順を経て、開発したシステムが高い精度で動作することを確認した。
三浦 隆智; 工藤 淳也; 小山 大輔; 大部 智行; 佐本 寛孝
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
東海再処理施設では、1977年から2007年までに、商業用発電炉(BWR,PWR)や新型転換炉ふげん等の使用済燃料を約1,140トン再処理した。廃止措置に移行した2018年から、リスク低減のため施設に保有する高放射性廃液(HALW)のガラス固化処理を最優先に取り組んできている。使用済燃料の再処理に伴い発生したHALWには、核分裂生成物(FP)等に加え、極微量のウランやプルトニウムを含む不溶解性残渣(スラッジ)が存在している。通常時ではHALW中のU, Puの濃度が非常に低いため、HALWが臨界に至ることは考え難い。また、事故時にHALWの冷却機能が喪失し、蒸発乾固に至る過程を考慮した場合においても、中性子吸収効果の高いFPが共存しているため、HALWが臨界に至ることは考え難い。これらを定量的に確認するために、HALWの蒸発によりU, Pu濃度が上昇し、乾固に至るまでの過程における臨界安全評価を実施した。本評価では、HALWを溶液系とスラッジ系、それぞれ無限体系モデルで、U, Pu, FPの存在比を分析データやORIGEN計算結果に基づき保守的に設定し、蒸発乾固に伴う溶液の濃縮による濃度変化に対して、無限増倍率を計算し、臨界未満の状態が維持されることを確認した。また、溶液系,スラッジ系の両系を考慮した2層の無限平板モデルでも、未臨界状態が維持されることを確認した。これにより、東海再処理施設においては、高放射性廃液の蒸発乾固の過程における臨界は想定されないことを確認した。
 Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant太田 雅和; 高原 省五; 吉村 和也; 長久保 梓; 廣内 淳; 林 奈穂; 阿部 智久; 舟木 泰智; 永井 晴康
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 264, p.107198_1 - 107198_15, 2023/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0(Environmental Sciences)福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPP)事故時に環境中に放出され、陸面に沈着した放射性核種について、大気中に再浮遊した Csの吸引は現在における主要な被ばく経路の一つである。再浮遊では、風による土壌粒子の巻き上げが主なメカニズムとされてきた。一方、FDNPP事故後の研究から、帰宅困難区域(DRZ)などの農村部においては、真菌類による胞子放出が大気中
Csの吸引は現在における主要な被ばく経路の一つである。再浮遊では、風による土壌粒子の巻き上げが主なメカニズムとされてきた。一方、FDNPP事故後の研究から、帰宅困難区域(DRZ)などの農村部においては、真菌類による胞子放出が大気中 Cs濃度に影響を及ぼす可能性が示唆されてきた。本研究は、土壌粒子および真菌類胞子としての
Cs濃度に影響を及ぼす可能性が示唆されてきた。本研究は、土壌粒子および真菌類胞子としての Cs再浮遊を計算するモデルを開発し、これをDRZ内に適用することで、これら再浮遊過程の大気中濃度への影響評価を試みた。モデル計算の結果から、土壌粒子の再浮遊は冬から春に観測された大気中
Cs再浮遊を計算するモデルを開発し、これをDRZ内に適用することで、これら再浮遊過程の大気中濃度への影響評価を試みた。モデル計算の結果から、土壌粒子の再浮遊は冬から春に観測された大気中 Csの主要因となったものの、夏から秋に観測された高濃度を再現できないことが示された。真菌類からの胞子状
Csの主要因となったものの、夏から秋に観測された高濃度を再現できないことが示された。真菌類からの胞子状 Csの放出を考慮することで、この夏から秋の高濃度事象は概ねモデルで再現された。解析結果から、真菌類胞子への
Csの放出を考慮することで、この夏から秋の高濃度事象は概ねモデルで再現された。解析結果から、真菌類胞子への Csの蓄積と、農村部に特徴づけられる高い胞子放出率が夏から秋の大気中
Csの蓄積と、農村部に特徴づけられる高い胞子放出率が夏から秋の大気中 Csに寄与している可能性が見出された。DRZ内には依然として未除染の森林が存在しているため、この真菌類胞子の大気中
Csに寄与している可能性が見出された。DRZ内には依然として未除染の森林が存在しているため、この真菌類胞子の大気中 Csへの寄与は今後将来も継続する可能性がある。
Csへの寄与は今後将来も継続する可能性がある。
笛田 和希*; 小宮 樹*; 蓑毛 健太*; 堀江 憲路*; 竹原 真美*; 山崎 信哉*; 塩津 弘之; 大貫 敏彦*; Grambow, B.*; Law, G. T. W.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 328, p.138566_1 - 138566_12, 2023/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:52.26(Environmental Sciences)Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) derived radioactive Cs-rich microparticles (CsMPs) present a potential health risk through inhalation. Despite their occurrence in indoor environments impacted by the FDNPP accident, little is known about their prevalence. In this study, we quantitatively analyse the distribution and number of CsMPs in indoor dust samples collected from an elementary school located 2.8 km to the southwest of FDNPP. The school had remained untouched until 2016. Then, using a modified version of the autoradiography based "quantifying CsMPs (mQCP) method," we collected samples and determined the number of CsMPs and Cs radioactive fraction (RF) values of the microparticles (defined as total Cs activity from CsMPs / bulk Cs activity of entire sample). The numbers of CsMPs were determined to be 653 - 2570 particles/g and 296 - 1273 particles/g on the first and second floors of the school, respectively. The corresponding RFs ranged between 6.85 - 38.9 % and 4.48 - 6.61 %, respectively. The number of CsMPs and RF values in additional outdoor samples near the school building were and 23 - 63 particles/g and 1.14 - 1.61 %, respectively. The CsMPs were most abundant on the School's first floor near to the entrance, and the relative abundance was high near to the stairs on the second floor, indicating a likely CsMP dispersion path through the building. Additional wetting of the indoor samples combined with autoradiography revealed that indoor dusts had a distinct absence of intrinsic, soluble Cs species like CsOH. Combined, the results indicate that a significant amount of poorly soluble CsMPs were likely contained in initial radioactive airmass plumes from the FDNPP and that the microparticles could penetrate buildings. Clean-up plans for buildings / residential areas impacted by CsMP containing plumes, and monitoring of areas re-opened to the public, should take account of CsMPs in dusts.
鈴木 誠矢; 荒井 陽一; 岡村 信生; 渡部 雅之
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.839 - 848, 2023/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)福島第一原子力発電所の事故で発生した燃料デブリは、溶融した核燃料物質と原子炉の構造材等で構成された酸化物が多くを占めているため、環境温度の変化により岩石のように劣化する可能性が高い。燃料デブリは10年以上水冷されているが、季節や昼夜の温度変化の影響を少なからず受けていることから、燃料デブリの経年変化挙動を評価するためには環境温度の変化を考慮することが不可欠である。仮に燃料デブリの劣化が進んでいる場合、微粉化した放射性物質が冷却水中に溶出して取出し作業に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、環境温度の繰り返し変化がクラックの発生に与える影響に着目して、燃料デブリの模擬体を用いた加速試験を実施した。その結果、クラックは温度変化を重ねることで増加することを確認し、燃料デブリの簿擬態は熱膨張と収縮による応力により脆化することが判明した。燃料デブリの物理学的な劣化挙動は岩石や鉱物に類似していることが確認され、模擬燃料デブリと環境のモデルでクラックの増加挙動を予測することが可能となった。
久保 光太郎
Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2023, p.7402217_1 - 7402217_12, 2023/06
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) is an effective methodology that could be used to improve the safety of nuclear power plants in a reasonable manner. Dynamic PRA, as an advanced PRA allows for more realistic and detailed analyses by handling time-dependent information. However, the applications of this method to practical problems are limited because it remains in the research and development stage. This study aimed to investigate the possibility of utilizing dynamic PRA in risk-informed decision-making. Specifically, the author performed an accident sequence precursor (ASP) analysis on the failure of emergency diesel generators that occurred at Unit 1 of the Tomari Nuclear Power Plant in Japan using dynamic PRA. The results were evaluated by comparison with the results of simplified classical PRA. The findings indicated that dynamic PRA may estimate lower risks compared with those obtained from classical PRA by reasonable modeling of alternating current power recovery. The author also showed that dynamic PRA can provide detailed information that cannot be obtained with classical PRA, such as uncertainty distribution of core damage timing and importance measure considering the system failure timing.
吉田 一雄; 玉置 等史; 桧山 美奈*
JAEA-Research 2023-001, 26 Pages, 2023/05
再処理施設の過酷事故の一つである高レベル放射性廃液貯槽の冷却機能喪失による蒸発乾固事故では、沸騰により廃液貯槽から発生する硝酸-水混合蒸気とともにルテニウム(Ru)の揮発性の化学種が放出される。このためリスク評価の観点からは、Ruの定量的な放出量の評価が重要な課題である。再処理施設のリスク評価の精度向上に資するため、計算プログラムを用いて当該事故時でのソースタームを解析的に評価する手法の整備を進めている。提案する解析手法では、まず廃液貯槽の沸騰をSHAWEDで模擬する。模擬結果の蒸気発生量等を境界条件としてMELCORにより施設内の蒸気等の流れに沿って各区画内の熱流動状態を模擬する。さらに各区画内の熱流動状態を境界条件としてSCHERNを用いてRuを含む硝酸、NO 等の化学挙動を模擬し、施設外への放射性物質の移行量(ソースターム)を求める。本報では、仮想の実規模施設での当該事故を想定して、これら3つの計算プログラム間でのデータの授受を含めて解析事例を示す。
等の化学挙動を模擬し、施設外への放射性物質の移行量(ソースターム)を求める。本報では、仮想の実規模施設での当該事故を想定して、これら3つの計算プログラム間でのデータの授受を含めて解析事例を示す。
北垣 徹; Krasnov, V.*; 池田 篤史
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 576, p.154224_1 - 154224_14, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:53.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear fuel debris is a complex material containing a wide range of elements, compounds, and radiation. This complexity renders all the stages of the treatment of nuclear fuel debris extremely difficult and troublesome in the technical context. The whole treatment of nuclear fuel debris is also an extremely long-term process for tens of thousands of years, during which the aging of nuclear fuel debris is an unavoidable but critical issue. This applies to the decommissioning of the damaged reactors of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F). This review article aims at collecting and summarizing the knowledge and information about the aging of materials containing nuclear fuels (fuel-containing materials) formed as a result of the accident at ChNPP-4 in the light of the decommissioning of 1F and assessing the potential effects of aging on the nuclear fuel debris remaining in the damaged 1F reactors.
長谷 竹晃; 相樂 洋*; 小菅 義広*; 能見 貴佳; 奥村 啓介
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(4), p.460 - 472, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper provides an overview of the applicability of the Differential Die-Away Self-Interrogation (DDSI) technique for quantification of spontaneous fissile nuclides in fuel debris at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. In this research, massive fuel debris stored in a canister was evaluated, and the void space of the canister was assumed to be filled with water for wet storage and air for dry storage. The composition of fuel debris was estimated based on elements such as the inventory in the reactor core and operation history. The simulation results show that for wet storage, the DDSI technique can properly evaluate the neutron leakage multiplication and quantify spontaneous fissile nuclides with a total measurement uncertainty (TMU) of approximately 8%. For dry storage, the known-alpha technique, which was previously established, can be applied to quantify spontaneous fissile nuclides with a TMU of approximately 4%. In both cases, the largest uncertainty factor is the variation in water content in the canister. In the case of wet storage, the uncertainty could be significantly increased in cases where the fuel debris is extremely unevenly distributed in the canister.
Dong, F.*; Chen, S.*; 出町 和之*; 吉川 雅紀; 関 暁之; 高屋 茂
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 404, p.112161_1 - 112161_15, 2023/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:90.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)To ensure nuclear safety, timely and accurate anomaly detection is of utmost importance in the daily condition monitoring of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs), as any slight anomaly in a plant may result in an irreversible and serious accident, as well as high costs of maintenance and management. Nevertheless, due to the unique inherent attributes of anomalies, the difficulty of automatic detection in NPPs is increased. Previous model-driven anomaly detection approaches required skilled priori knowledge, leading to their limited usability. Commonly adopted deep learning-based data-driven anomaly detection approaches may not easily acquire the most relevant features when dealing with sensor data containing redundant information with uneven distribution of anomalies. To alleviate these issues, this paper propose an attention-based time series model for anomaly detection to ensure safety in NPPs. First, we employ one-dimension convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) backbone for feature extraction to preserve original inherent features of time series inputs. Subsequently, we originally adopt soft-attention mechanism to automatically extract the most relevant temporal features considering the specificity of anomaly detection in NPPs. The performance of the proposed model was experimentally validated on the High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) anomaly case dataset simulated using the analytical code. The experimental results indicate that the proposed model was capable of detecting anomalies in NPPs with superior performance to the baseline model, while ensuring fast detection at short time steps.
日高 昭秀
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332, p.1607 - 1623, 2023/03
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)福島第一原子力発電所事故時に初めて放出されたタイプA Cs含有微粒子(以下、タイプA)の生成機構について、これまで様々な生成機構説が議論されてきた。筆者は、3号機の非常用ガス処理系(SGTS)のHEPAフィルタが水素爆発時に溶融して微粒化したことにより生成したと考えた。しかし、その仮説は、熱水力と大気拡散及びその学際領域にも及んで複雑であり、まだ推論が多く含まれている。このため、今後は様々な専門家による検証や、タイプA生成に関する再現試験が必要と考えた。さらに、もし仮説が正しいとした場合、HEPAフィルタは安全上重要な機器であり、水素爆発防止対策やHEPAフィルタの設計等にも影響するかもしれないと考え始めていた。そこで、これらの検討を進めるため、タイプAの生成機構に関して、総合的に解説したレビューが必要との結論に至った。本稿では、筆者がこれまでに執筆した論文等に基づき、仮説の根拠、検証及びその仮説が正しいとした時に実際に何が起こったと考えられるか、今後の課題、原子力安全性の更なる向上の観点からの提言について述べる。
友常 祐介; 矢嶋 まゆみ; 奥野 浩; 山本 一也
労働安全衛生研究, 16(1), p.29 - 43, 2023/02
2011年3月に起きた東日本大震災に伴い発生した東京電力福島第一原子力発電所における事故において、日本原子力研究開発機構では最初の1年間にのべ約45,000人の職員が本来の職場を離れて電話相談,一時帰宅支援,環境モニタリングなどの支援業務に従事した。特に、住民と直接に接する電話相談に従事した職員には、感情労働に伴うストレスがかかった。同機構の核燃料サイクル工学研究所ではこれらの支援業務に従事した職員に対して、組織的なメンタルヘルスケアを行った。本論文では今回の活動を「支援者の支援」の具体例と位置づけ、原子力災害において住民等の支援を行う職員のメンタルヘルスについて考察した。
外川 織彦; 大倉 毅史; 木村 仁宣
JAEA-Review 2022-049, 76 Pages, 2023/01
原子力施設の建設前及び操業開始後には、平常運転時及び事故時に対する環境影響評価が行われる。これらは、周辺住民の安全の確認と安心の醸成を図ることを主たる目的としている。環境影響評価には、施設周辺の環境モニタリング等による観測・測定と計算モデルによるモデル推定が用いられ、状況や必要性などに応じてそれらのどちらか、あるいは両方を併用して実施される。本報告書では、原子力施設の環境影響評価において利用される観測・測定とモデル推定について、青森県六ヶ所村再処理施設を主たる例として、まず各々の方法、役割と長短、相互の関係性を調査する。次に、観測・測定データとモデル推定結果の代表的な用途例を示し、使用に際しての留意点などを検討する。最後に、観測・測定とモデル推定の高度化や両者の融合という今後の方向性を記述する。
久保 光太郎; 田中 洋一*; 石川 淳
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part O; Journal of Risk and Reliability, 11 Pages, 2023/00
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:0.01(Engineering, Multidisciplinary)Nuclear power plants are critical infrastructures that provide electricity. However, accidents in nuclear power plants can cause considerable consequences such as the release of radioactive materials. Therefore, appropriately managing their risk is necessary. Various nuclear regulatory agencies employ probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) to effectively evaluate risks in nuclear power plants. Dynamic PRA has gained popularity because it allows for more realistic assessment by reducing the assumptions and engineering judgments related to time-dependent failure probability and/or human-action reliability in the conventional PRA methodology. However, removing all assumptions and engineering judgments is difficult; thus, the risk analyst, e.g., the regulator, must understand their effects on the assessment results. This study focuses on "risk dilution," which emerges from the assumptions about uncertainty. Dynamic PRA of a station blackout sequence in a boiling-water reactor was performed using the dynamic PRA tool, namely, Risk Assessment with Plant Interactive Dynamics (RAPID) and the severe-accident code Thermal-Hydraulic Analysis of Loss of Coolant, Emergency Core Cooling, and Severe Core Damage version 2 (THALES2), which altered the correlation parameters among the uncertainties of the events that occurred in sequence. The results demonstrated that the conditional core-damage probability and mean value of the core-damage time varied from 0.27 to 0.47 and from 7.1 to 8.7 h, respectively. When the dynamic PRA results are used for risk-informed decision making, the decision maker should adequately consider the effect of risk dilution.
吉田 一雄; 玉置 等史; 桧山 美奈*
JAEA-Research 2022-011, 37 Pages, 2022/12
再処理施設の過酷事故の一つとして高レベル放射性廃液貯槽の冷却機能喪失による蒸発乾固事故が想定される。再処理廃液の沸騰段階での放射性物質の気相部への移行のメカニズムは、沸騰によって生成される飛沫のうち比較的小さい粒径の液滴のエアロゾル化と、揮発性化学種の温度上昇に伴う気化である。気相に移行した放射性物質は、沸騰により発生する硝酸-水混合蒸気や硝酸塩の熱分解による脱硝反応で生じるNO などとともに貯槽から流出し、施設内を移行し一部は施設外に放出されると想定される。当該事故で生じるこれらの諸事象は、すべて貯槽内の廃液の沸騰を起源とするため、それによって生じるリスクを精度良く評価するには、汎用性のある計算プログラムを用いた貯槽内の熱水力的及び化学的挙動の定量的な模擬が不可欠である。これを目的として再処理廃液の沸騰を模擬する計算プログラム: SHAWED (
などとともに貯槽から流出し、施設内を移行し一部は施設外に放出されると想定される。当該事故で生じるこれらの諸事象は、すべて貯槽内の廃液の沸騰を起源とするため、それによって生じるリスクを精度良く評価するには、汎用性のある計算プログラムを用いた貯槽内の熱水力的及び化学的挙動の定量的な模擬が不可欠である。これを目的として再処理廃液の沸騰を模擬する計算プログラム: SHAWED (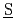 imulation of
imulation of 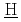 igh-level radio
igh-level radio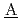 ctive
ctive 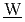 aste
aste 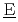 vaporation and
vaporation and 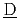 ryness)を開発した。本報では、当該事故のリスク評価に資するために、模擬対象とする事象の特徴をもとに沸騰及びそれに伴う諸事象の模擬に必要な主要な解析モデルを説明するとともに、具体的な模擬事例を示す。
ryness)を開発した。本報では、当該事故のリスク評価に資するために、模擬対象とする事象の特徴をもとに沸騰及びそれに伴う諸事象の模擬に必要な主要な解析モデルを説明するとともに、具体的な模擬事例を示す。
萩原 大樹; 近藤 啓悦; 日高 昭秀
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(12), p.5905 - 5914, 2022/12
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:53.91(Chemistry, Analytical)Radiocesium-bearing microparticles (CsMPs) were released from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant during the 2011 accident. We examined the CsMP formation process by analyzing Type-A particles and conducting in situ glass fiber experiments. The results demonstrated that heating glass fibers to 450 C - 800
C - 800 C formed spherical particles, their morphologies and elemental compositions were similar to those of actual CsMPs. The mock-up particles size was strongly dependent on the glass-fiber thickness. Our findings reveal that glass fibers can form microparticles after being exposed to high temperatures.
C formed spherical particles, their morphologies and elemental compositions were similar to those of actual CsMPs. The mock-up particles size was strongly dependent on the glass-fiber thickness. Our findings reveal that glass fibers can form microparticles after being exposed to high temperatures.
山根 祐一
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1331 - 1344, 2022/11
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)反応度または外部中性子源強度の瞬時変化の後で生じる準定常状態における中性子計数率もしくはそのシミュレーションデータの経時変化に基づいて体系の反応度を評価した。その評価は準定常状態における出力の方程式に基づいて行った。研究の目的は中性子計数率の複雑な経時変化から適時に反応度を評価する方法を開発することである。開発した手法を中性子計数率のシミュレーションデータに適用した。そのデータは一点炉動特性コードAGNESによる計算とポワソン分布を持つ乱数によって作成したものである。さらにTRACYを用いて取得された未臨界実験データにも適用した。その結果、反応度の評価値と基準値の差は-10$以上の条件でのシミュレーションデータに対しては5%程度以下の差であり、-1.4$と-3.1$での実験データに対しては、7%程度以下であった。条件変化の数十秒後に反応度を評価できる可能性がこれにより示された。
中村 秀夫; Bentaib, A.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Ruyer, P.*; Mascari, F.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Adorni, M.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Topical Issues in Nuclear Installation Safety; Strengthening Safety of Evolutionary and Innovative Reactor Designs (TIC 2022) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/10
The WGAMA activity achievements have been published as technical reports, becoming reference materials to discuss innovative methods, materials and technologies in the fields of thermal-hydraulics, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and severe accidents (SAs). The International Standard Problems (ISPs) and Benchmarks of computer codes have been supported by a huge amount of the databases for the code validation necessary for the reactor safety assessment with accuracy. The paper aims to review and summarize the recent WGAMA outcomes with focus on new advanced reactor applications including small modular reactors (SMRs). Particularly, discussed are applicability of major outcomes in the relevant subjects of passive system, modelling innovation in CFD, severe accident management (SAM) countermeasures, advanced measurement methods and instrumentation, and modelling robustness of safety analysis codes. Although large portions of the outcomes are considered applicable, design-specific subjects may need careful considerations when applied. The WGAMA efforts, experiences and achievements for the safety assessment of operating nuclear power plants including SA will be of great help for the continuous safety improvements required for the advanced reactors including SMRs.